|
Size: 10003
Comment:
|
Size: 10167
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 7: | Line 7: |
| This page describes the automated construction of a cell-cell interaction database by filtering existing curated protein-protein interaction (PPI) data. Cell-cell interactions are important for understanding tissue organization. We and others have built cell-cell interaction databases ([[#ref1|1]],[[#ref2|2]],[[#ref3|3]],[[#ref4|4]],[[#ref5|5]]). The resource available from this website represents an automatically built and expanded set of protein-protein interactions that can mediate cell-cell communication. | This page describes the automated construction of a cell-cell interaction database by filtering existing curated protein-protein interaction (PPI) data. Cell-cell interactions are important for understanding tissue organization. We and others have built cell-cell interaction databases ([[#ref1|1]],[[#ref2|2]],[[#ref3|3]],[[#ref4|4]],[[#ref5|5]]). The resource available from this website represents an automatically built set of protein-protein interactions that can mediate cell-cell communication that is expanded compared to previous databases we have built. |
| Line 77: | Line 77: |
| 1. [[attachment:receptor_ligand_interactions_mitab_v1.0_April2017.txt.zip|Ligand - Receptor interaction set]] - tab delimited file in [[https://psicquic.github.io/MITAB25Format.html|mitab 2.5]] format containing the following columns: | 1. [[attachment:receptor_ligand_interactions_mitab_v1.0_April2017.txt.zip|Ligand - Receptor interaction set]] ([[attachment:receptor_ligand_interactions_mitab_v1.0_April2017.txt.gz| alternate file compatible with windows]] ) - tab delimited file in [[https://psicquic.github.io/MITAB25Format.html|mitab 2.5]] format containing the following columns: |
Cell-Cell Interaction Database
Contents
Overview
This page describes the automated construction of a cell-cell interaction database by filtering existing curated protein-protein interaction (PPI) data. Cell-cell interactions are important for understanding tissue organization. We and others have built cell-cell interaction databases (1,2,3,4,5). The resource available from this website represents an automatically built set of protein-protein interactions that can mediate cell-cell communication that is expanded compared to previous databases we have built.
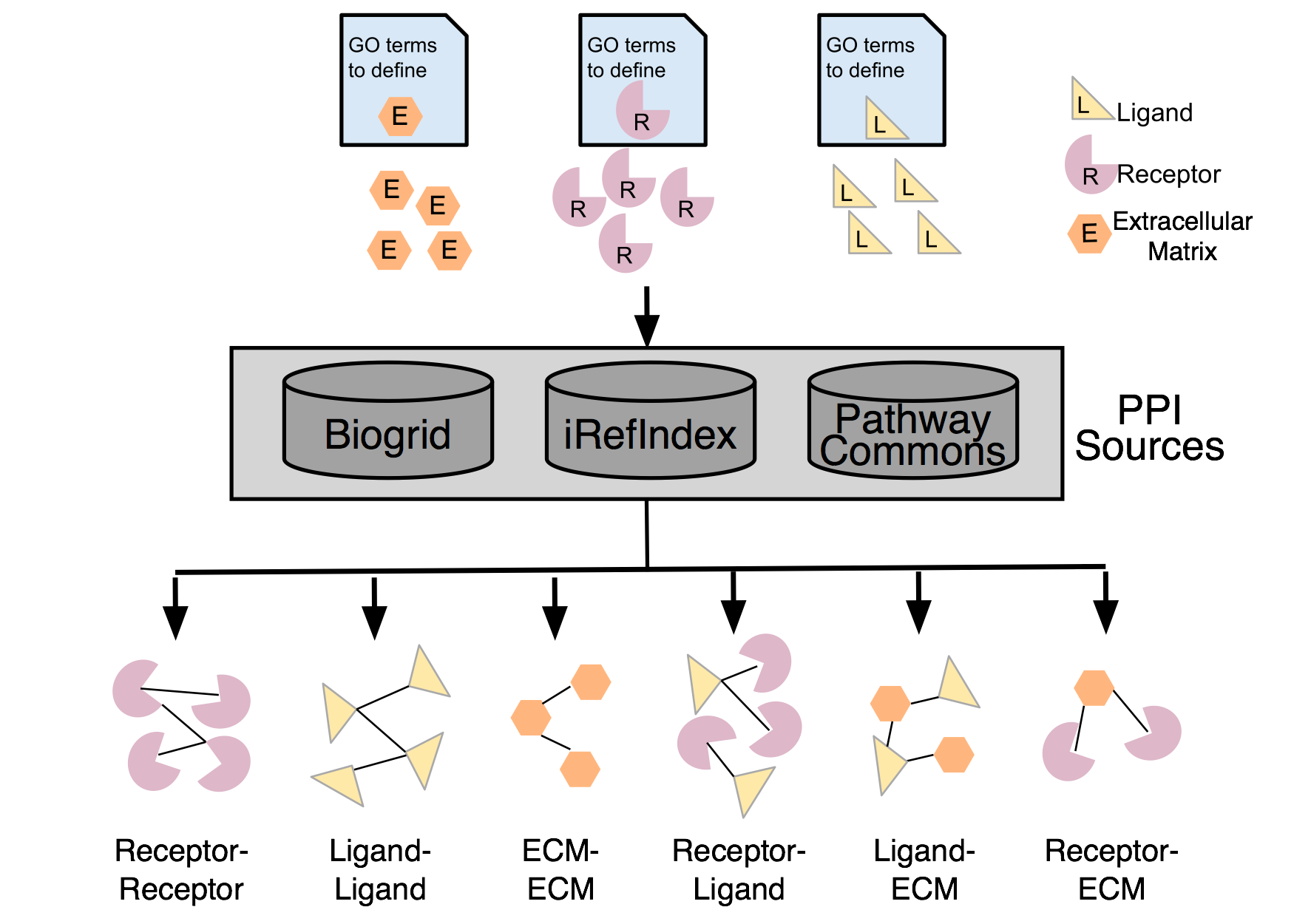
Defining Receptor and Ligands
Receptors
Receptor genes were defined based on the union of the annotations from
the set of Gene Ontology (GO) terms(6,7):
GO:0043235 - receptor complex,
GO:0008305 - integrin complex,
GO:0072657 - protein localized to membrane
GO:0043113 - receptor clustering
GO:0004872 - receptor activity,
GO:0009897 - external side of plasma membrane)
UniProt annotations
- search term -"Receptor [KW-0675]" go:0005886 organism:human.
This created a set of 4364 receptor genes (prior to manual curation)
Ligands
Ligand genes were defined based on the union of the below annotations
GO:0005102 - receptor binding
the set of proteins labelled as secreted in the Secretome dataset (http://www.proteinatlas.org/humanproteome/secretome) (8).
This created a set of 3209 Ligand genes (prior to manual curation)
Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) genes were defined based on the union of the annotations from
GO:0031012 - extracellular matrix
GO:0005578 - proteinacious extracellular matrix
GO:0005201 - extracellular matrix structural constituent
GO:1990430 - extracellular matrix protein binding
GO:0035426 - extracellular matrix cell signalling
This created a set of 433 ECM genes (prior to manual curation)
Manual Curation
ECM, Receptor and ligand lists were manually curated
- genes that were neither receptors or ligands were removed
- misclassified genes were moved to the correct list (i.e. receptors found on the ligand list or vice versa)
After curation, the resulting ligand, receptor and ECM sets consisted of:
- Receptors - 1851 genes
- Ligands - 1593 genes
- ECM - 433 genes
In each of the above sets there are genes that are part of other sets (e.g. a gene can be ECM and ligand at the same time)
Interaction Data
The set of protein interactions were downloaded from:
iRefIndex (version 14) (9). - all BioGRID interactions were excluded from the iRefIndex set as we imported the original source.
BioGRID (version 3.4.147)(11).
The entire interaction set was filtered to only include interactions that contained receptor-ligand, receptor-receptor, ligand-ligand, receptor-ecm, ligand-ecm or ecm-ecm interactions where the receptor, ligands and ecm were defined by the above lists.
The resulting Receptor-Ligand network contained 2,593 unique proteins and 38,446 unique interactions (115,900 interaction total)
Download Data
Molecule Definition files
Ligands - table of ligands. (contains HGNC symbol and classification (Ligand, Ligand/ECM, Ligand/Receptor, Ligand/ECM/Receptor)
Receptors - table of receptors. (contains HGNC symbol and classification (Receptor, Receptor/ECM, Ligand/Receptor, Ligand/ECM/Receptor)
ECM - table of ECM. (contains HGNC symbol and classification (ECM, ECM/Receptor, ECM/Ligand, Ligand/ECM/Receptor)
Protein types - table of unique set of receptor, ligand and ECM genes (contains HGNC symbol as well as classification (Receptor, Ligand, ECM, ECM/Receptor, ECM/Ligand, Receptor/Ligand, Ligand/ECM/Receptor)
Interaction files
Version 1.0 - Built April 25, 2017 and contains iRefIndex version 14, Pathway Commons version 8 and BioGRID version 3.4.147
Ligand - Receptor interaction set (alternate file compatible with windows ) - tab delimited file in mitab 2.5 format containing the following columns:
AliasA - main Alias for molecule A (often the recognized gene symbol)
AliasB- main Alias for molecule B (often the recognized gene symbol)
uidA - unique identifier for molecule A (depending on the source database this can be one of the following types uniprot, refseq, entrez gene id, ensembl)
uidB - unique identifier for molecule A (depending on the source database this can be one of the following types uniprot, refseq, entrez gene id, ensembl)
altA - list of alternate identifiers for molecule A.
altB - list of alternate identifiers for molecule B.
aliasA - list of alternate aliases for molecule A.
aliasB - list of alternate aliases for molecule B.
method - list of psi-mi terms indicating experimental methods used to discover interaction.
author - text listing authors
pmids - list of pmids associated with the interaction.
taxa - taxon id for molecule A.
taxb - taxon id for molecule B.
interactionType - list of psi-mi terms indicating the type of interactions it is.
sourcedb - source database.
interactionIdentifier - source database interaction identifier
confidence - confidence of interaction as supplied by database source
References
Qiao W, Wang W, Laurenti E, Turinsky AL, Wodak SJ, Bader GD, Dick JE, Zandstra PW Intercellular network structure and regulatory motifs in the human hematopoietic system
PubmedKirouac DC, Ito C, Csaszar E, Roch A, Yu M, Sykes EA, Bader GD, Zandstra PW. Dynamic interaction networks in a hierarchically organized tissue. Mol Syst Biol. 2010 Oct 5;6:417
PubmedYuzwa SA, Yang G, Borrett MJ, Clarke G, Cancino GI, Zahr SK, Zandstra PW, Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Proneurogenic Ligands Defined by Modeling Developing Cortex Growth Factor Communication Networks. Neuron. 2016 Sep 7;91(5):988-1004
PubmedRamilowski JA, Goldberg T, Harshbarger J, Kloppmann E, Lizio M, Satagopam VP, Itoh M, Kawaji H, Carninci P, Rost B, Forrest AR. A draft network of ligand-receptor-mediated multicellular signalling in human. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 22;6:7866.
PubmedRieckmann JC, Geiger R, Hornburg D, Wolf T, Kveler K, Jarrossay D, Sallusto F, Shen-Orr SS, Lanzavecchia A, Mann M, Meissner F. Social network architecture of human immune cells unveiled by quantitative proteomics. Nat Immunol. 2017 May;18(5):583-593. PMID: 28263321.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000 May;25(1):25-9
PubmedThe Gene Ontology Consortium. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D331-D338
PubmedUhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C, Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, Olsson I, Edlund K, Lundberg E, Navani S, Szigyarto CA, Odeberg J, Djureinovic D, Takanen JO, Hober S, Alm T, Edqvist PH, Berling H, Tegel H, Mulder J, Rockberg J, Nilsson P, Schwenk JM, Hamsten M, von Feilitzen K, Forsberg M, Persson L, Johansson F, Zwahlen M, von Heijne G, Nielsen J, Pontén F. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015 Jan 23;347(6220)
PubmedRazick S, Magklaras G, Donaldson IM. iRefIndex: a consolidated protein interaction database with provenance. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Sep 30;9:405
PubmedCerami EG, Gross BE, Demir E, Rodchenkov I, Babur O, Anwar N, Schultz N, Bader GD, Sander C. Pathway Commons, a web resource for biological pathway data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D685-90.2010 Nov 10.
PubmedStark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher L, Breitkreutz A, Tyers M. BioGRID: a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D535-9.
Pubmed
