|
Size: 42316
Comment:
|
Size: 44744
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 412: | Line 412: |
| <<BR>><<BR>><<BR>><<BR>> <<BR>><<BR>><<BR>><<BR>> <<BR>><<BR>><<BR>><<BR>> |
|
| Line 415: | Line 417: |
| <<anchor(expressionpanel)>> | <<Anchor(expressionpanel)>> |
| Line 417: | Line 419: |
| * There are two different types of Expression Viewers, each is represented as a separate tab in data panel: * EM Overlap - shows the expression of genes in the overlap (intersection) of all the genesets selected * EM Geneset - shows the expression of genes of the union of all the genesets selected. * Features of the Expression Viewer include: * Normalization |
{{attachment:EM_expressionviewer_panel.png|Screenshot Heatmap Expression Viewer Panel}} * There are two different types of Expression Viewers, each is represented as a separate tab in data panel: EM Overlap and EM Gene set. The only difference between the two expression viewers is the set of gene listed. 1. '''EM Overlap Expression Viewer''' - shows the expression of genes in the overlap (intersection) of all the genesets selected 1. '''EM Geneset Expression Viewer''' - shows the expression of genes of the union of all the genesets selected. 1. '''Normalization''' |
| Line 425: | Line 427: |
| * Sorting | 1. '''Sorting''' |
| Line 430: | Line 432: |
| * Save Expression Set | 1. '''Save Expression Set''' |
| Line 432: | Line 434: |
| 1. '''Export Expression Set (PDF)''' * The user can save the expression heatmap currently being viewed in the expression viewer as pdf file. Unfortunately the pdf version is not perfect. The column titles are at the bottom instead of the top of the heatmap. Due to limitations with the current library being used we are unable to fix this in cityscape 2.8.3 but hope to have a better pdf representation in the EM version for Cytoscape 3.0. |
|
| Line 460: | Line 464: |
| <<anchor(parampanel)>> | <<Anchor(parampanel)>> |
| Line 466: | Line 470: |
| 1. P-value Cut-off tuner - allows you to adjust the p-value threshold used to filter the gene sets. | 1. '''P-value Cutoff''' tuner - allows you to adjust the p-value threshold used to filter the gene sets. |
| Line 470: | Line 474: |
| 1. Q-value Cut-off tuner - allows you to adjust the q-value threshold used to filter the gene sets. | 1. '''Q-value Cutoff''' tuner - allows you to adjust the q-value threshold used to filter the gene sets. |
| Line 474: | Line 478: |
| 1. Similarity Cut-off tuner - allows you to adjust the similarity threshold used to filter the gene set overlaps (edges). | 1. '''Similarity Cutoff''' tuner - allows you to adjust the similarity threshold used to filter the gene set overlaps (edges). |
| Line 480: | Line 484: |
| 1. Heatmap Autofocus | 1. '''Heatmap Autofocus''' |
| Line 484: | Line 488: |
| 1. Default Sorting order - in the [[#expressionpanel|expression viewer]] genes can be sorted by Hierarchical clustering, Ranks, Columns, or No sort. To set the default change selection. 1. Default Distance Metric - for hierarchical clustering there are three available distance metrics that can be used to compute distances between genes. By default this is set of pearson correlation. Update this parameter if you which to use one of the other distance metrics. |
1. '''Default Sorting order''' - in the [[#expressionpanel|expression viewer]] genes can be sorted by Hierarchical clustering, Ranks, Columns, or No sort. To set the default change selection. 1. '''Default Distance Metric''' - for hierarchical clustering there are three available distance metrics that can be used to compute distances between genes. By default this is set of pearson correlation. Update this parameter if you which to use one of the other distance metrics. <<BR>><<BR>><<BR>> |
| Line 517: | Line 522: |
| * Requirements: 1. Enrichment Map v1.3 or higher 1. Commandtool - available from Cytsocape App store |
* Requirements: 1. Enrichment Map v1.3 or higher 1. Commandtool App - available from Cytsocape App store. Documentation can be found [[https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/cytoscape/utilities/index.html|here]] 1. GSEA results in an edb directory * command tool can be used from: 1. the command line * java -Xmx1G -jar "{path_to_cytoscape_dir}\cytoscape.jar" -p "{path_to_plugin_dir}\plugins" -S "{path_to_script_file}" 1. cytoscape command window * (Plugins->commandtool-->Command Window...) 1. script file * (Plugins->commandtool-->Run Script...) * Command Options {{{ enrichmentmap build: Build an enrichment map from GSEA results (in an edb directory) Arguments: [edbdir=value] --> REQUIRED [expressionfile=value] --> OPTIONAL [overlap=value] --> OPTIONAL [pvalue=value] --> OPTIONAL [qvalue=value] --> OPTIONAL [similaritymetric=value] --> OPTIONAL [combinedconstant=value] --> OPTIONAL }}} * Example Command (for command window) {{{ enrichmentmap build edbdir="{path_to_edb_directory}" pvalue=0.01 qvalue=0.1 overlap=0.5 similaritymetric="jaccard" expressionfile="{path_to_expression_file}" }}} |
| Line 534: | Line 566: |
{{attachment:GSEA_leadingedge.png|GSEA EM leading edge|align="left"}} 1. To access GSEA leading edge information click on an individual Node. Leading edge information is currently only available when looking at a single gene set. 1. In the Data Panel the expression profile for the selected gene set should appear in the ''EM GenesetExpression viewer'' tab. 1. Change the Normalization to your desired metric. 1. Change the Sorting method to ''GSEARanking''. 1. Genes part of the leading edge are highlighted in Yellow. |
Enrichment Map User Guide
Contents
Overview
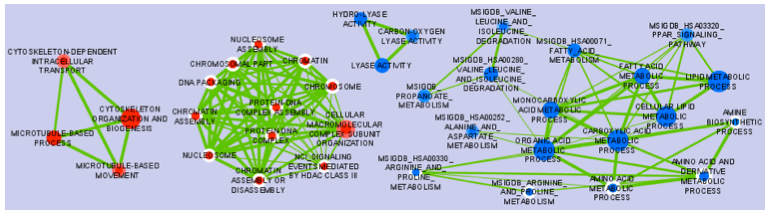
The Enrichment Map Cytoscape Plugin allows you to visualize the results of gene-set enrichment as a network. It will operate on any generic enrichment results as well as specifically on Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) results. Nodes represent gene-sets and edges represent mutual overlap; in this way, highly redundant gene-sets are grouped together as clusters, dramatically improving the capability to navigate and interpret enrichment results.
Gene-set enrichment is a data analysis technique taking as input
a (ranked) gene list, from a genomic experiment
- gene-sets, grouping genes on the basis of a-priori knowledge (e.g. Gene Ontology) or experimental data (e.g. co-expression modules)
and generating as output the list of enriched gene-sets, i.e. best sets that summarizing the gene-list. It is common to refer to gene-set enrichment as functional enrichment because functional categories (e.g. Gene Ontology) are commonly used as gene-sets.
Installation
The Enrichment Map Plugin requires Cytoscape Version 2.6.x. If you don't have Cytoscape or an older Version (2.5 or older), please download the latest Release from http://www.cytoscape.org/ and install it on your computer.
Download the Enrichment Map plugin from Software/EnrichmentMap and manually place the file EnrichmentMap.jar in the Cytoscape/plugins folder.
Quick Start Guide
Creating an Enrichment Map
You have a few different options:
- Load GSEA Results
- Load Generic Results
- Load David Results
- Load Bingo Results
The only difference between the above modes is the structure of the enrichment table(s). In either case, to use the plugin you will need the following files:
- file.gmt: gene-set to gene ID
- file.txt or .gct: expression matrix [OPTIONAL]
- file.txt or .xls (*): enrichment table(s)
(*) GSEA saves the enrichment table as a .xls file; however, these are not true Excel files, they are tab-separated text files with a modified extension; Enrichment Map does not work with "true" Excel .xls files.
If your enrichment results were generated from GSEA, you will just have to pick the right files from your results folder. If you have generated the enrichment results using another method, you will have to go to the Full User Guide, File Format section, and make sure that the file format complies with Enrichment Map requirements.
You can use the parameter defaults. For a more careful choice of the parameter settings, please go to the Full User Guide, Tips on Parameter Choice.
Graphical Mapping of Enrichment
- Nodes represent gene-sets.
- Edges represent mutual overlap.
- Enrichment significance (p-value) is conveyed as node colour intensity.
The enriched phenotype is conveyed by node colour hue.
Note: In standard two-class designs, where two phenotypes are compared (e.g. treated vs untreated) the colour hue conveys the enriched phenotype; this is equivalent to mapping enrichment in up- and down-regulated genes, if one of the two phenotypes is assumed as reference (e.g. untreated), and the other phenotype is the one of interest; in such a case, enriched in the phenotype of interest means up, and enrichment in the reference phenotype means down.
- Node size represents how many genes are in the gene-set.
Exploring the Enrichment Map
- The "Parameters" tab in the "Results Panel" on the right side of the window contains a legend mapping the colours to the phenotypes and displaying the parameters used to create the map (cut-off values and data files).
- The "Network" tab in the "Control Panel" on the left lists all available networks in the current session and at the bottom has a overview of the current network which allows to easily navigate in a network even at higher zoom levels by dragging the blue rectangle (the current view) over the network.
- Clicking on a node (the circle that represents a gene set) will open the "EM Geneset Expression Viewer" tab in the "Data Panel" showing a heatmap of the expression values of all genes in the selected gene set.
- Clicking on an edge (the line between two nodes) will open the "EM Overlap Expression Viewer" tab in the "Data Panel" showing a heatmap of the expression values of all genes both gene sets that are connected by this edge have in common.
- If several nodes and edges are selected (e.g. by dragging a selection box around the desired gene sets) the "EM Geneset Expression Viewer" will show the union of all genes in the selected gene sets and the "EM Overlap Expression Viewer" will show only those genes that all selected gene sets have in common.
Advanced tips
- With large networks and low zoom-levels Cytoscape automatically reduces the details (such as hiding the node labels and not showing the node borders). To override this mechanism click on "View / Show Graphics Details"
The VizMapper and the Node- and Edge Attribute Browser open up a lot more visualization options like linking the label size to Enrichment Scores or p-values. Refer to the Cytoscape manual at www.cytoscape.org for more information.
If you have used Genesets from GSEAs MSigDb, you can access additional informations for each gene set, by adding the a new property:
(Edit / Preferences / Properties... / Add -> enter property name: nodelinkouturl.MSigDb -> enter property value: http://www.broad.mit.edu/gsea/msigdb/cards/%ID%.html -> [
 ] Make Current Cytoscape Properties default -> (OK) ). Now you can right-click on a node and choose LinkOut/MSigDb to open the Database entry of the Geneset represented by that node in your Browser.
] Make Current Cytoscape Properties default -> (OK) ). Now you can right-click on a node and choose LinkOut/MSigDb to open the Database entry of the Geneset represented by that node in your Browser.
When loading GSEA results there is no need to specify each file. Use the GSEA RPT file to auto-populate all the file fields in the EM interface. Check out: How to use RPT files
You can specify more lax p-value, q-value and coefficient threshold initially and fine tune them after the network is created by adjusting them through the p-value, q-value and coefficient tuners in the results panel. Check out:How to use Parameters Panel
Full User Guide
File Formats
Gene sets file (GMT file)
- Each row of the geneset file represents one geneset and consists of:
- geneset name (--tab--) description (--tab--) a list of tab-delimited genes that are part of that geneset.
- The geneset names must be unique.
- The gene set file describes the genesets used for the analysis. These files can be obtained
directly downloading our monthly updated gene-set collections from Baderlab geneses collections. Description of sources and methods used to create collection can be found here
directly downloading gene-sets collected in the MSigDB
Note: if you use MSigDB Gene Ontology gene-sets, please consider that they do not include all annotations, as an evidence code filter is applied; if you are interested in achieving maximum coverage, download the original annotations
converting gene annotations / pathways from public databases
~-Note: if you are a R user, Bioconductor offers annotation packages such as GO.db, org.Hs.eg.db, KEGG.db
Expression Data file (GCT, TXT or RNK file) [OPTIONAL]
- The expression data can be loaded in three different formats: gct (GSEA file type), rnk (GSEA file type) or txt.
- The expression data serves two purposes:
- Gene sets are filtered based on the genes present in the expression file. For example, if Geneset X contains genes
- Expression data is not required. In the absence of an expression file Enrichment map will create a dummy expression file to associate with the data set. The dummy expression gives an expression value of 1 for all the genes associated with the enriched genesets in the Enrichment map.
GCT (GSEA file type)
GCT differs from TXT only because of two additional lines that are required at the top of the file.
- The GCT file contains two additional lines at the top of the file.
- The first line contains #1.2.
- The second line contains the number of data rows (tab) the number of data columns.
- The third line consists of column headings.
- name (--tab--) description (--tab--) sample1 name (--tab--) sample2 name …
- Each line of expression file contains a:
- name (--tab--) description (--tab--) followed by a list of tab delimited expression values.
- NOTE: If the GCT file contains Probeset ID's as primary keys (e.g. as you had GSEA collapse your data file to gene symbols) you need to convert the gct file to use the same primary key as used in the gene sets file (GMT file). You have the following options:
- Use the GSEA desktop application: GSEA / Tools / Collapse Dataset
Run this Python script collapse_ExpressionMatrix.py using the Chip platform file that was used by GSEA.
RNK (GSEA file type)
RNK file is completely different from the GCT or TXT file. It represents a ranked list of genes containing only gene name and a rank or score.
- The first line contains column headings
- (For example:) Gene Name (--tab--) Rank Name
- Each line of RNK file contains a:
- name (--tab--) rank OR score
Additional Information on GSEA File Formats can be found here
TXT
- Basic file representing expression values for an experiment.
- The first line consists of column headings.
- name (--tab--) description (--tab--) sample1 name (--tab--) sample2 name ...
- Each line of the expression file contains a:
- name (--tab--) description (--tab--) followed by a list of tab delimited expression values.
Enrichment Results files
GSEA result files
- For each analysis GSEA produces two output files. One representing the enriched genesets in phenotype A and the other representing the enriched genesets in phenotype B.
- These files are usually named "gsea_report_for_phenotypeA.Gsea.########.xls" and "gsea_report_for_phenotypeB.Gsea.########.xls"
- The files should be loaded in as is and require no pre-processing.
- There is no need to worry about which Enrichment Results Text box to put the two files. The phenotype is specified by the sign of the ES score and is computed internally by the program.
Additional Information on GSEA File Formats can be found here
Generic results files
- The generic results file is a tab delimited file with enriched gene-sets and their corresponding p-values (and optionally, FDR corrections)
- The Generic Enrichment Results file needs:
- gene-set ID (must match the gene-set ID in the GMT file),
- gene-set name or description,
- p-value,
- FDR correction value
- Phenotype: +1 or -1, to identify enrichment in up- and down-regulation, or, more in general, in either of the two phenotypes being compared in the two-class analysis
- +1 maps to red
- -1 maps to blue
Notes:
- description and FDR columns can have empty or NA values, but the column and the column header must exist
- if no value is provided under phenotype, Enrichment Map will assume there is only one phenotype, and will map enrichment p-values to red
DAVID Enrichment Result File
- Available only in v1.0 or higher
When using DAVID as the analysis type there is no requirement to enter either a gmt file or an expression file. Both are options if the user wishes to add them to the analysis.
The DAVID Enrichment Result File is a file generated by the DAVID Functional Annotation Chart Report and consists of the following fields: Important: Make sure you are using CHART Report and NOT a Clustered Report
- Category (DAVID category, i.e. Interpro, sp_pir_keywords, ...)
- Term - Gene set name
- Count - number of genes associated with this gene set
- Percentage (gene associated with this gene set/total number of query genes)
- P-value - modified Fisher Exact P-value
- Genes - the list of genes from your query set that are annotated to this gene set.
- List Total - number of genes in your query list mapped to any gene set in this ontology
- Pop Hits - number of genes annotated to this gene set on the background list
- Pop Total - number of genes on the background list mapped to any gene set in this ontology.
- Fold enrichment
- Bonferroni
- Benjamini
- FDR
Notes:
- The DAVID option expects a file as generated by the DAVID web interface.
DISCLAIMER : In the absence of a gmt gene sets are constructed based on the field Genes in the DAVID output. This only considers the genes entered in your query set and not the genes in your background set. This will drastically affect the amount of overlap you see in the resulting Enrichment Map.
See here for tutorial on how to generate David output files for Enrichment maps
BiNGO Enrichment Result File
- Available only in v1.2 or higher
When using BiNGO as the analysis type there is no requirement to enter either a gmt file or an expression file. Both are options if the user wishes to add them to the analysis.
The BiNGO Enrichment Result File is a file generated by the BiNGO cytoscape plugin and consists of the following fields: Important: When running BiNGO make sure to check off "Check Box for saving data"
The first 20 lines of BiNGO output file list parameters used for the analysis and are ignored by the Enrichment map plugin
- GO-ID - Gene set name
- p-value - hypergeometric or binomial Exact P-value
- corr p-value - corrected p-value
- x - number of genes in your query list mapped to this gene-set
- n - number of genes in the background list mapped to this gene-set
- X - number of genes annotated to this gene set on the background list
- N - number of genes on the background list mapped to any gene set in this ontology.
- Description - gene list description
- Genes - the list of genes from your query set that are annotated to this gene set.
Notes:
- The BiNGO option expects a file as generated by the BiNGO Cytsocape Plugin.
DISCLAIMER : In the absence of a gmt gene sets are constructed based on the field Genes in the BiNGO output. This only considers the genes entered in your query set and not the genes in your background set. This will drastically affect the amount of overlap you see in the resulting Enrichment Map.
See here for tutorial on how to generate Bingo output files for Enrichment maps
RPT files
- A special trick for GSEA results, in any GSEA analysis an rpt file is created that specifies the location of all files (including the gmt, gct, results files, phenotype specification, and rank files).
- Any of the Fields under the dataset tab (Expression, Enrichment Results 1 or Enrichment Results 2) will accept an rpt file and populate GMT, Expression, Enrichment Results 1, Enrichment Results 2, Phenotypes, and Ranks the values for that dataset.
- A second rpt file can be loaded for dataset 2. It will give you a warning if the GMT file specified is different than the one specified in dataset 1. You will have the choice to use the GMT for data set 1, data set 2 or abort the second rpt load.
- An rpt file is a text file with following information (parameters surrounded by " ' ' '" are those that EM uses):
'''producer_class''' xtools.gsea.Gsea
'''producer_timestamp''' 1367261057110
param collapse false
param '''cls''' WHOLE_PATH_TO_FILE/EM_EstrogenMCF7_TestData/ES_NT.cls#ES24_versus_NT24
param plot_top_x 20
param norm meandiv
param save_rnd_lists false
param median false
param num 100
param scoring_scheme weighted
param make_sets true
param mode Max_probe
param '''gmx''' WHOLE_PATH_TO_FILE/EM_EstrogenMCF7_TestData/Human_GO_AllPathways_no_GO_iea_April_15_2013_symbol.gmt
param gui false
param metric Signal2Noise
param '''rpt_label''' ES24vsNT24
param help false
param order descending
param '''out''' WHOLE_PATH_TO_FILE/EM_EstrogenMCF7_TestData
param permute gene_set
param rnd_type no_balance
param set_min 15
param include_only_symbols true
param sort real
param rnd_seed timestamp
param nperm 1000
param zip_report false
param set_max 500
param '''res''' WHOLE_PATH_TO_FILE/EM_EstrogenMCF7_TestData/MCF7_ExprMx_v2_names.gct
file WHOLE_PATH_TO_FILE/EM_EstrogenMCF7_TestData/ES24vsNT24.Gsea.1367261057110/index.html- Parameters used by EM and their meaning:
producer_class - can be xtools.gsea.Gsea or xtools.gsea.GseaPreranked
if xtools.gsea.Gsea:
- get expression file from res parameter in rpt
- get phenotype information from cls parameter in rot
if xtools.gsea.GseaPreranked:
- No expression file
- use rnk as the expression file from rnk parameter in rot
- set phenotypes to na_pos and na_neg.
- NOTE: if you want to make using an rpt file easier for GSEAPreranked there are two additional parameters you can add to your rpt file manually that the rpt function will recognize.
To do less manual work while creating Enrichment Maps from pre-ranked GSEA, add the following optional parameters to your rpt file: param(--tab--)phenotypes(--tab--){phenotype1}_versus_{phenotype2} param(--tab--)expressionMatrix(--tab--){path_to_GCT_or_TXT_formated_expression_matrix}
- producer_timestamp - needed to find the directory with the results files
- cls - path to class/phenotype file with information regarding the phenotypes:
- path/classfilename.cls#phenotype1_versus_phenotype2
- EM get the path to the class file and also pulls the phenotype1 and phenotype2 from the above field
- gmx - path to gmt file
- rpt_label - name of analysis and name of directory that GSEA creates to hold the results. Used when constructing the path to the results directory.
- out - path to directory where GSEA will put the output directory. Used when constructing the path to the results directory.
- res - path to expression file.
- rpt Searches for the following results files:
Enrichment File 1 --> {out}(--File.separator--){rpt_label} + "." + {producer_class} + "." + {producer_timestamp}(--File.separator--) "gsea_report_for_" + phenotype1 + "_" + timestamp + ".xls"
Enrichment File 2 --> {out}(--File.separator--){rpt_label} + "." + {producer_class} + "." + {producer_timestamp}(--File.separator--) "gsea_report_for_" + phenotype2 + "_" + timestamp + ".xls"
Ranks File --> {out}(--File.separator--){rpt_label} + "." + {producer_class} + "." + {producer_timestamp}(--File.separator--) "ranked_gene_list_" + phenotype1 + "_versus_" + phenotype2 +"_" + timestamp + ".xls"; - If the enrichments and rank files are not found in the above path then EM replaces the out directory with the path to the given rpt file and tries again.
- if you would like to create your own rpt file for your own analysis pipeline you can put your own values for the above used parameters.
- If your analysis only creates one enrichment file you can make a copy of enrichment file 1 in the path of enrichment file 2 with no consequences for EM running.
EDB File (GSEA file type)
- Contained in the GSEA results folder is an edb folder. In the edb folder there are the following files:
- results.edb
- gene_sets.gmt
- classfile.cls [Only in a GSEA analysis. Not in a GSEAPreranked analysis]
- rankfile.rnk
- If you specify the results.edb file in any of the Fields under the dataset tab (Expression, Enrichment Results 1 or Enrichment Results 2) the gmt and enrichment files fields will be automatically populated.
If you want to associate an expression file with the analysis it needs to be loaded manually as described here.
* NOTE: The gene_sets.gmt file contained in the edb directory is filtered according to the expression file. If you are doing a two dataset analysis where the expression files are from different platforms or contain different sets of genes the edb gene_sets.gmt file can not be used as genes found in one analysis might be lacking in the other. In this case use the original gmt file (prior to GSEA filtering) and EM will filter each the gene sets separately according to each dataset.
Advanced Settings - Additional Files
- For each dataset there are additional parameters that the user can set but are not required.
- The advanced parameters include:
Ranks file - file specifying the ranks of the genes in the analysis
This file has the format specified in the above section - gene (--tab--) rank or score. Seehere for details.
Phenotypes (phenotype1 versus phenotype2)
- By default the phenotypes are set to Up and Down but in the advanced setting mode the user can change these to any desired text.
All of these fields are populated when the user loads the input files using the rpt option.
Parameters
Node (Gene Set inclusion) Parameters
- Node specific parameters filter the gene sets included in the enrichment map
- For a gene set to be included in the enrichment map it needs to pass both p-value and q-value thresholds.
P-value
- All gene sets with a p-value with the specified threshold or below are included in the map.
FDR Q-value
- All gene sets with a q-value with the specified threshold or below are included in the map.
- Depending on the type of analysis the FDR Q-value used for filtering genesets by EM is different
- For GSEA the FDR Q-value used is 8th column in the gsea_results file and is called "FDR q-val".
- For Generic the FDR Q-value used is 4th column in the generic results file.
- For David the FDR Q-value used is 12th column in the david results file and is called "Benjamini".
- For Bingo the FDR Q-value used is 3rd column in the Bingo results file and is called "core p-value"
Edge (Gene Set relationship) Parameters
- An edge represents the degree of gene overlap that exists between two gene sets, A and B.
- Edge specific parameters control the number of edges that are created in the enrichment map.
- Only one coefficient type can be chosen to filter the edges
Jaccard Coefficient
Jaccard Coefficient = [size of (A intersect B)] / [size of (A union B)]
Overlap Coefficient
Overlap Coefficient = [size of (A intersect B)] / [size of (minimum( A , B))]
Combined Coefficient
- the combined coefficient is a merged version of the jacquard and overlap coefficients.
- the combined constant allows the user to modulate reciprocally the weights associated with the jacquard and overlap coefficients.
- When k = 0.5 the combined coefficient is the average between the jacquard and overlap.
Jaccard Coefficient = [size of (A intersect B)] / [size of (A union B)]
Overlap Coefficient = [size of (A intersect B)] / [size of (minimum( A , B))]
Combined Constant = k
Combined Coefficient = (k * Overlap) + ((1-k) * Jaccard)
Tips on Parameter Choice
P-value and FDR Thresholds
GSEA can be used with two different significance estimation settings: gene-set permutation and phenotype permutation. Gene-set permutation was used for Enrichment Map application examples.
Gene-set Permutation
Here are different sets of thresholds you may consider for gene-set permutation:
- Very permissive:
p-value < 0.05
FDR < 0.25
- Moderately permissive:
p-value < 0.01
FDR < 0.1
- Moderately conservative:
p-value < 0.005
FDR < 0.075
- Conservative:
p-value < 0.001
FDR < 0.05
For high quality, high coverage transcriptomic data, the number of enriched terms at the very conservative threshold is usually 100-250 when using gene-set permutation.
Phenotype Permutation
- Recommended:
p-value < 0.05
FDR < 0.25
In general, we recommend to use permissive thresholds only if your having a hard time finding any enriched terms.
Jaccard vs. Overlap Coefficient
- The Overlap Coefficient is recommended when relations are expected to occur between large-size and small-size gene-sets, as in the case of the Gene Ontology.
- The Jaccard Coefficient is recommended in the opposite case.
- When the gene-sets are about the same size, Jaccard is about the half of the Overlap Coefficient for gene-set pairs with a small intersection, whereas it is about the same as the Overlap Coefficient for gene-sets with large intersections.
- When using the Overlap Coefficient and the generated map has several large gene-sets excessively connected to many other gene-sets, we recommend switching to the Jaccard Coefficient.
Overlap Thresholds
- 0.5 is moderately conservative, and is recommended for most of the analyses.
- 0.3 is permissive, and might result in a messier map.
Jaccard Thresholds
- 0.5 is very conservative
- 0.25 is moderately conservative
Interfaces
The Input Panel
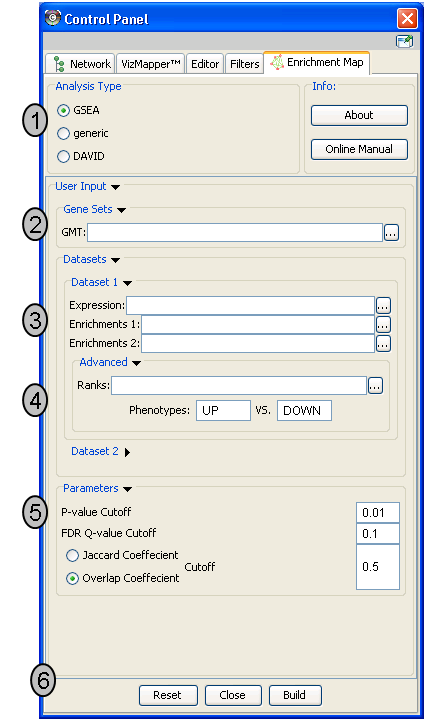
Analysis Type
- There are two distinct types of Enrichment map analyses, GSEA or Generic.
GSEA - takes as inputs the output files created in a GSEA analysis. File formats are specific to files created by GSEA. The main difference between this and generic is the number and format of the Enrichment results files. GSEA analysis always has two enrichment results files, one for each of the phenotypes compared.
Generic - takes as inputs the same file formats as a GSEA analysis except the Enrichment results file is a different format and there is only one enrichment file. Generic File description
DAVID - (implemented in v1.0 and higher) has no gmt or expression file requirement and takes as input enrichment result file as produced by DAVID David Enrichment Result File description
- There are two distinct types of Enrichment map analyses, GSEA or Generic.
Genesets - path to gmt file describing genesets. User can browse hard drive to find file by pressing ... button.
Dataset 1 - User can specify expression and enrichment files or alternatively, an rpt file which will populate all the fields in genesets,dataset # and advanced sections.
Advanced - Initially collapsed (expand by clicking on arrow head directly next to Advanced), users have the option of modifying the phenotype labels or loading gene rank files.
Parameters - User can specify p-value, fdr and overlap/jaccard cutoffs. Choosing Optimal parameter values
Actions - The user has three choices, Reset (clears input panel), Close (closes input panel), and Build Enrichment map (takes all parameters in panel and builds an Enrichment map)
The Data Panel
- The bottom (south) panel.
Expression Viewer

- There are two different types of Expression Viewers, each is represented as a separate tab in data panel: EM Overlap and EM Gene set. The only difference between the two expression viewers is the set of gene listed.
EM Overlap Expression Viewer - shows the expression of genes in the overlap (intersection) of all the genesets selected
EM Geneset Expression Viewer - shows the expression of genes of the union of all the genesets selected.
Normalization
- Data as is - represents the data as it was loaded
- Row Normalize Data - for each value in a row of expression the mean of the row is subtracted followed by division by the row's standard deviation.
- Log Transform Data - takes the log of each expression value
Sorting
- Hierarchical cluster - as computed using Pearson correlation of the entire expression set.
- If rank files for the data sets are provided at input they will show up as 'Dataset 1 Ranking' and 'Dataset 2 Ranking' and by selecting them the user will be able to sort the expression accordingly
- if an expression value does not have a corresponding rank in the ranking file its expression does not appear in the heatmap.
Add Ranking ... - allows user to upload an additional rank file (in the appropriate format,as outlined in Rank file descriptions). There is no limit on the number of rank files that are uploaded. The user is required to give a name to the rank file.
Save Expression Set
- The user can save the subset of expression values currently being viewed in the expression viewer as txt file.
Export Expression Set (PDF)
- The user can save the expression heatmap currently being viewed in the expression viewer as pdf file. Unfortunately the pdf version is not perfect. The column titles are at the bottom instead of the top of the heatmap. Due to limitations with the current library being used we are unable to fix this in cityscape 2.8.3 but hope to have a better pdf representation in the EM version for Cytoscape 3.0.
Node Attributes
- For each Enrichment map created the following attributes are created for each node:
- EM#_Name - the gene set name
EM#_Formatted_name - a wrapped version of the gene set name so it is easy to visualize.
Note: This is the default label of the node but some users find it easier to arrange the network when the name is not wrapped. If this is the case in the vizmapper the user can switch the label mapping from EM#_formatted_name to EM#_name.
- EM#_GS_DESCR - the gene set description (as specified in the second column of the gmt file)
- EM#_Genes - the list of genes that are part of this gene set.
- Additionally there are attributes created for each dataset (a different set for each dataset if using two dataset mode):
- EM#_pvalue_dataset(1 or 2) - Gene set p-value, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_qvalue_dataset(1 or 2) - Gene set q-value, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_Colouring_dataset(1 or 2) - Enrichment map parameter calculated using the formula 1-pvalue multiplied by the sign of the ES score (if using GSEA mode) or the phenotype (if using the Generic mode)
- GSEA specific attributes (these attributes are not populated when creating an enrichment map using the generic mode)
- EM#_ES_dataset(1 or 2) - Enrichment score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_NS_dataset(1 or 2) - Normalized Enrichment score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
- EM#_fwer_dataset(1 or 2) - Family-wise error score, as specified in GSEA enrichment result file.
Edge Attributes
- For each Enrichment map created the following attributes are created for each edge:
- EM#_Overlap_size - the number of genes associated with the overlap of the two genesets that this edge connects.
- EM#_Overlap_genes - the names of the genes that are associated with the overlap of the two genesets that this edge connects.
EM#_similarity_coefficient - the calculated coefficient for this edge.
The Results Panel
- The right (east) panel
Parameters pane
- Reference panel containing legends, slider bars for the user to modify p-value and q-value cut-offs, parameters used for the analysis
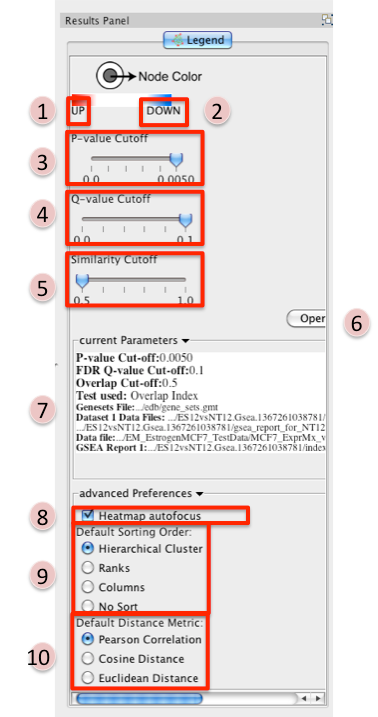
- Phenotype 1
- Phenotype 2
P-value Cutoff tuner - allows you to adjust the p-value threshold used to filter the gene sets.
- By moving the slider to the left you can decrease the p-value threshold causing nodes (and their edges) to be removed from the network.
- Moving the slider back to the right will restore the nodes (and their edges).
- You can NOT increase the p-value threshold above what you specified when you built the network.
Q-value Cutoff tuner - allows you to adjust the q-value threshold used to filter the gene sets.
- By moving the slider to the left you can decrease the q-value threshold causing nodes (and their edges) to be removed from the network.
- Moving the slider back to the right will restore the nodes (and their edges).
- You can NOT increase the q-value threshold above what you specified when you built the network.
Similarity Cutoff tuner - allows you to adjust the similarity threshold used to filter the gene set overlaps (edges).
- By moving the slider to the right you can increase the similarity threshold causing edges to be removed from the network.
- Moving the slider back to the left will restore the edges.
- You can NOT decrease the similarity threshold below what you specified when you built the network.
- Button to launch index of GSEA results in a web browser.
- List of parameters used to create the EM.
Heatmap Autofocus
- selected by default
When you click on any node or edge in the network EM automatically updates the expression viewer and makes the focus of the Data panel the overlap expression viewer. When using other plugins in conjunction with EM this feature can get cumbersome.
- To turn this off unselect "heatmap Autofocus".
Default Sorting order - in the expression viewer genes can be sorted by Hierarchical clustering, Ranks, Columns, or No sort. To set the default change selection.
Default Distance Metric - for hierarchical clustering there are three available distance metrics that can be used to compute distances between genes. By default this is set of pearson correlation. Update this parameter if you which to use one of the other distance metrics.
PostAnalysis Input Panel
To access the post-analysis, follow the path: Menu: Plugin / Enrichment Map / Post Analysis.
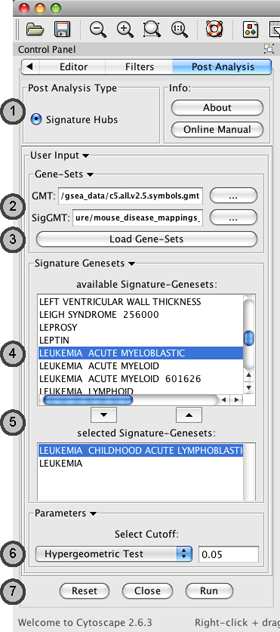
Post Analysis Type
- Currently there is only one Type of Post Analysis available:
Signature Hubs - calculates the overlap between genesets of the current Enrichment Map and a number of selected external genesets.
Gene Sets
- The user needs to supply two geneset-files (both in the gmt format):
GMT - Enrichment Genesets; the same geneset gmt file as used to create the Enrichment Map (this field will be usually already populated)
SigGMT - the gmt file with the Signature-Genesets
Load Genesets should be pressed after the file with the Signature-Genesets has been selected. This will populate the list of available Signature Genesets.
Available Signature Genesets – Once the genesets are loaded, this box will contain a list of all genesets defined in the SigGMT file. Click to highlight the desired geneset(s).
- To highlight more than one geneset at a time, the user can click while pressing the [SHIFT]-, [COMMAND]- or [CTRL]-keys (depending on the Operating System).
Selected Signature Genesets – The Signature Hub analysis will be performed with all genesets in this list. The user can use the down- and up-buttons to move highlighted genesets from one list to the other.
Parameters – The User can choose a method and a cutoff for generating an edge between a signature-geneset and an enrichment geneset. The following methods are available:
Hypergeometric Test is the probability (p-value) to find an overlap of k or more genes between a signature geneset and an enrichment geneset by chance.
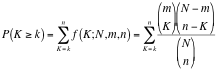
with:
k (successes in the sample) : size of the Overlap,
n (size of the sample) : size of the Signature geneset
m (total number of successes) : size of the Enrichment Geneset
N (total number of elements) : size of the union of all Enrichment Genesets
Number of common Genes
directed Overlap is the fraction of the intersection of both genesets in respect to the Enrichment Geneset.
Actions - The user has three choices, Reset (clears input panel), Close (closes input panel), and Run (takes all parameters in panel and performs the Post-Analysis)
The post-analysis p-values can be accessed by: select the following attribute for display: "EM1_Overlap_Hypergeom_pVal" (Data Panel: Edge Attribute Browser tab, attribute selection icon)
Additional Features
Launch Enrichment Map from the command line
- Requirements:
- Enrichment Map v1.3 or higher
Commandtool App - available from Cytsocape App store. Documentation can be found here
- GSEA results in an edb directory
- command tool can be used from:
- the command line
- java -Xmx1G -jar "{path_to_cytoscape_dir}\cytoscape.jar" -p "{path_to_plugin_dir}\plugins" -S "{path_to_script_file}"
- cytoscape command window
(Plugins->commandtool-->Command Window...)
- script file
(Plugins->commandtool-->Run Script...)
- the command line
- Command Options
enrichmentmap build: Build an enrichment map from GSEA results (in an edb directory)
Arguments:
[edbdir=value] --> REQUIRED
[expressionfile=value] --> OPTIONAL
[overlap=value] --> OPTIONAL
[pvalue=value] --> OPTIONAL
[qvalue=value] --> OPTIONAL
[similaritymetric=value] --> OPTIONAL
[combinedconstant=value] --> OPTIONAL- Example Command (for command window)
enrichmentmap build edbdir="{path_to_edb_directory}" pvalue=0.01 qvalue=0.1 overlap=0.5 similaritymetric="jaccard"
expressionfile="{path_to_expression_file}"
Distinct Species or Platform Analysis
Bulk Enrichment Map Build
Calculate Gene set relationships
GSEA Leading Edge Functionality
For every gene set that is tested for significance using GSEA there is a set of proteins in that gene set defined as the Leading Edge. According to GSEA the leading edge is:
"the subset of members that contribute most to the ES. For a positive ES, the leading edge subset is the set of members that appear in the ranked list prior to the peak score. For a negative ES, it is the set of members that appear subsequent to the peak score."
- In essence, the leading edge is the set of genes that contribute most to the enrichment of the gene set.
For Enrichment Map, leading edge information is extracted from the gsea enrichment results files from the column denoted as Rank at Max. Rank at max is the rank of the gene where the ES score has the maximal value, i.e. the peak ES score. Everything with a better rank than the rank at max is part of the leading edge set.
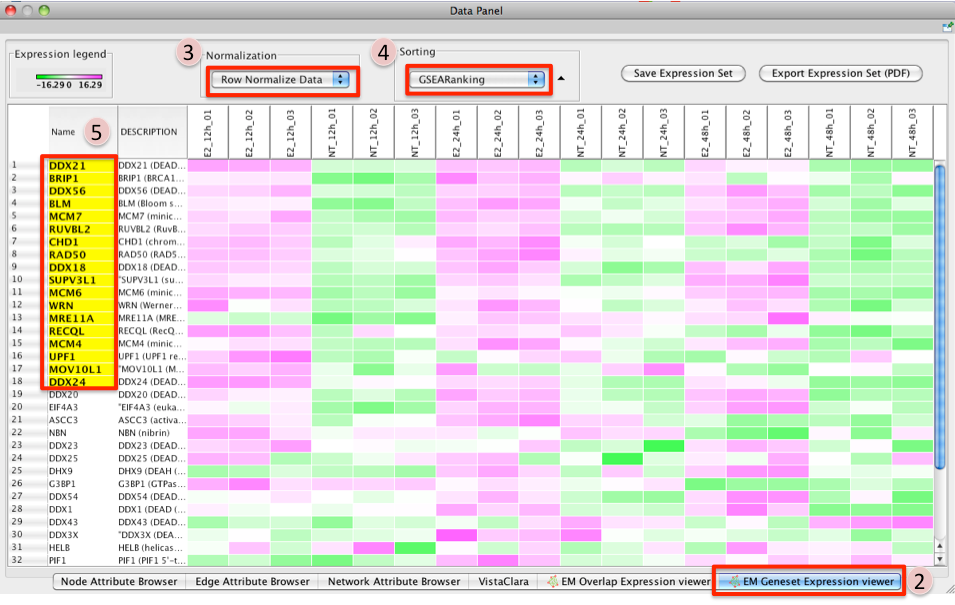
- To access GSEA leading edge information click on an individual Node. Leading edge information is currently only available when looking at a single gene set.
In the Data Panel the expression profile for the selected gene set should appear in the EM GenesetExpression viewer tab.
- Change the Normalization to your desired metric.
Change the Sorting method to GSEARanking.
- Genes part of the leading edge are highlighted in Yellow.
Customizing Defaults with Cytoscape Properties
The Enrichment Map Plugin evaluates a number of Cytoscape Properties with which a user can define some customized default values.
These can be added and changed with the Cytoscape Preferences Editor (Edit / Preferences / Properties...) or by directly editing the file cytoscape.props within the .cytoscape folder in the User's HOME directory.
Supported Cytoscape Properties are:
- EnrichmentMap.default_pvalue
- Default P-value cutoff for Building Enrichment Maps
Default Value: 0.05
valid Values: float >0.0, <1.0
- EnrichmentMap.default_qvalue
- Default Q-value cutoff for Building Enrichment Maps
- Default Value: 0.25
valid Values: float >0.0, <1.0
- EnrichmentMap.default_overlap
- Default Overlap coefficient cutoff for Building Enrichment Maps
- Default Value: 0.50
valid Values: float >0.0, <1.0
- EnrichmentMap.default_jaccard
- Default Jaccard coefficient cutoff for Building Enrichment Maps
- Default Value: 0.25
valid Values: float >0.0, <1.0
- EnrichmentMap.default_overlap_metric
- Default choice of similarity metric for Building Enrichment Maps
Default Value: Jaccard
valid Values: Jaccard, Overlap
- EnrichmentMap.default_sort_method
- Set the default sorting in the legend/parameters panel to Hierarchical Clustering,
- Ranks (default the first rank file, if no ranks then it is no sort), Column (default is the first column) or no sort.
Default Value: Hierarchical Cluster
valid Values: Hierarchical Cluster, Ranks, Columns, No Sort
- Set the default sorting in the legend/parameters panel to Hierarchical Clustering,
- EnrichmentMap.hieracical_clusteting_theshold
- Threshold for the maximum number of Genes before a dialogue opens to confirm if clustering should be performed.
- Default Value: 1000
- valid Values: Integer
- nodelinkouturl.MSigDb.GSEA Gene sets
LinkOut URL for MSigDb.GESA Gene sets.
Default Value: http://www.broad.mit.edu/gsea/msigdb/cards/%ID%.html
- valid Values: URL
- EnrichmentMap.disable_heatmap_autofocus
- Flag to override the automatic focus on the Heatmap once a Node or Edge is selected.
Default Value: FALSE
valid Values: TRUE, FALSE
FAQ
Q: One of my enrichment map clusters has so much overlapping, I'm having a hard time interpreting it.
A: Quickest solutions:- Menu: Layout / Scale to expand the sub-network of interest (it will reduce clutter, but may take a lot of space)
- Results Panel: reduce the Q-value cutoff (it will make the sub-network less crowded, at the expense of the less relevant gene-sets)
- Clone the sub-network into a new network and use organic layout (organic layout has less clutter than force directed)
Use the Software/WordCloudPlugin to summarize the node labels
- Make an enrichment map only of that sub-network using the Jaccard coefficient
- this needs some scripting: you have to restrict the GMT to the gene-sets in the sub-network and make a new enrichment map selecting the Jaccard coefficient (instead of Overlap).
- Jaccard usually works better with super-connected sub-networks, i.e. the ones arising when you have lots of GO-derived redundancy
